Impetigo in children is a skin infection caused by bacteria. It’s common during childhood, although anyone can get it. It’s a highly contagious condition , so it’s important to know the symptoms of impetigo in children and the most effective treatment.
What is impetigo in children?
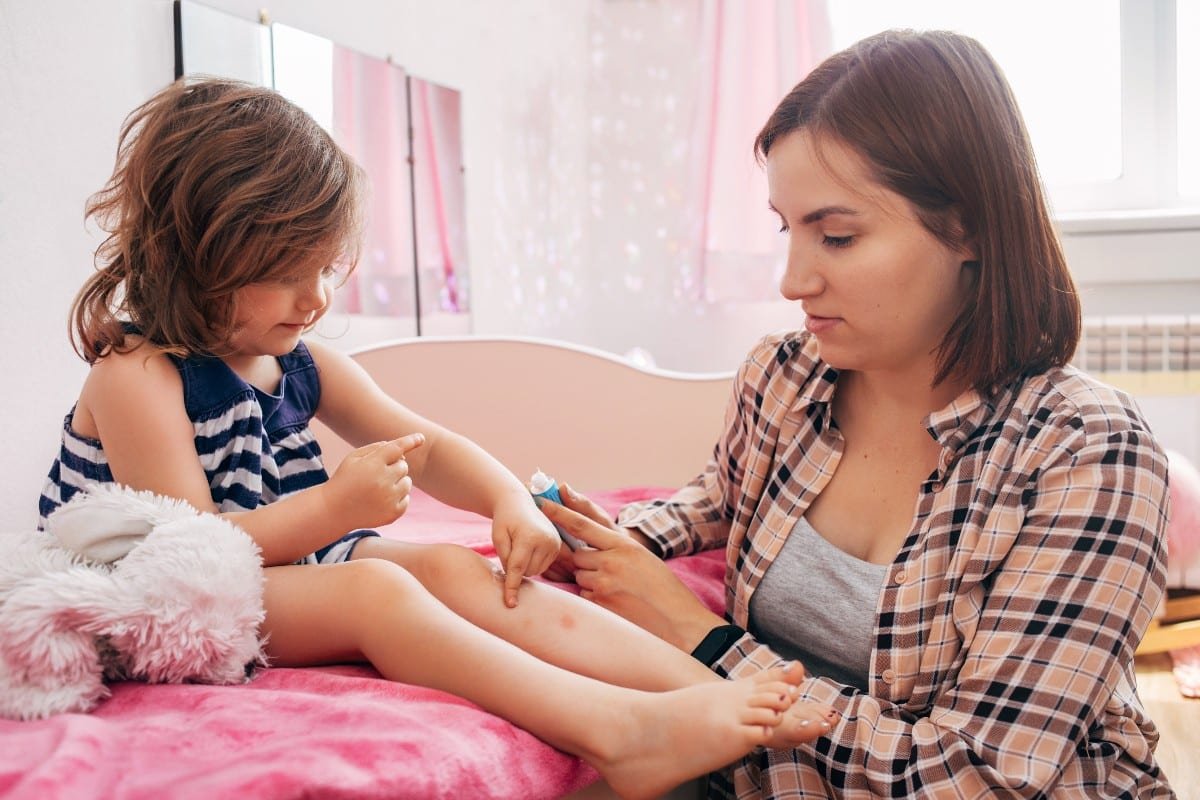
Impetigo is a skin infection that causes blisters or ulcers that may be itchy or painful. When a child scratches and tears the blisters, scabs may also appear.
It is generally not a serious condition, although it is important to detect it early to prevent it from worsening.
The most vulnerable group to childhood impetigo is those between 2 and 5 years of age, although cases of impetigo can occur in babies as well as in adults.
It’s worth noting that impetigo in children tends to be more common during warmer weather, when outdoor activities can contribute to skin scratches that eventually become infected.
Is impetigo contagious in children?
Impetigo is a highly contagious condition . Its main route of spread is through physical contact . If your child has this infection, it’s best to avoid direct contact. It’s also not recommended that they return to school until the symptoms have cleared.
Causes of impetigo in children
These are the main causes of impetigo.
Bacteria responsible
Impetigo originates after a skin injury, such as an insect bite, a small cut, or a scratch. This injury becomes an entry point for certain bacteria that eventually cause the infection.
Two bacteria cause this condition:
- Staphylococcus aureus, also known as staph.
- Group A streptococcus.
Risk factors
Certain factors have been observed that increase the risk of contracting the disease. One of the most common problems during childhood is problems related to skin irritations, such as eczema.
Additionally, an insect bite or irritation caused by poison ivy can act as a trigger. For example, if a child tends to scratch a blister that develops until it becomes infected and develop into impetigo.
Humid climates can promote bacterial buildup. Meanwhile, warm weather in spring and summer is also considered another risk factor for impetigo in children, as it encourages outdoor activities that involve wounds or scratches on the skin.
Symptoms of impetigo in children
These are the main symptoms of impetigo on the skin in children :
- It may start with a small red dot on the skin.
- Over time, it becomes a blister with fluid inside.
- The blister eventually breaks down to form what is known as a honey scab. This is a yellowish crust resembling the color of honey.
- In more serious cases, the infection may lead to fever.
How to identify impetigo on the skin in children
This disease is characterized by the form it takes on the skin. However, its diagnosis should always be made by a medical professional, who will be able to identify it during a regular consultation.
Since this is a common disease, additional testing is not usually required to confirm the infection. However, occasionally, a specialist may request a sample for culture.
Types of impetigo in children
Do you know the different types of impetigo in children? The following types exist in total:
Bullous impetigo
Its name comes from the trace left behind by the infection. Bullous impetigo causes large blisters filled with clear fluid to form on the skin. These blisters eventually burst, resulting in red, moist sores.
Non-bullous impetigo
This is the most common. Small blisters appear on the skin that burst, causing fluid to ooze out. Over time, this fluid forms a yellowish crust, similar in color to honey or brown sugar.
Facial impetigo in children
Among the types of impetigo, we find facial impetigo, which typically appears on a child’s face. The nose, mouth, and ears are the areas of the face most at risk for it.
Impetigo labialis in children
Lip impetigo is the formation of blisters or crusts around a child’s lips. They often appear at the corners of the mouth.
Stages of impetigo in children
There are distinct phases of the disease. This is how the impetigo infection progresses.
1. Initial stage
In the early stages, the skin rash will be barely visible. A few red spots may appear.
2. Development of blisters and scabs
Visible blisters appear within a few days. Depending on the type of infection, these may burst easily or remain intact for a few days. Eventually, they may burst, forming scabs.
3. Resolution and healing
Once the infection disappears, the wounds will begin to heal. It’s a good idea to accompany the process with good hygiene in the area and some skin treatment if recommended by a medical specialist.
How is impetigo spread in children?
As we mentioned, childhood impetigo is highly contagious. It can be transmitted to other children as well as adults. Therefore, it is important to take extreme hygiene measures.
Forms of transmission
- Direct contact with the rash.
- Contact with the liquid inside the ampoule.
- Through towels, clothes, or clothing that have been handled by the child with impetigo.
- Through contaminated objects.
Prevention of contagion
It is recommended to avoid direct contact with the infected person until the rash clears. If the person is a child, it is advisable not to take them to school for a few days.
It’s a good idea to take extra hygiene measures at home. Wash your hands with soap and water, especially if you’ve come into contact with the infection. Sharing towels or kitchen utensils is not recommended. If it’s facial or lip impetigo, make sure tissues with mucus or tears from the child are thrown directly into the trash.
Treatment for impetigo in children
When it comes to neutralizing the infection, we can find two very effective treatments:
- When the disease is not too serious, topical treatments are often used . The most common form is an antibiotic cream applied to the affected area for five days.
- If the infection has spread to several parts of the body, oral antibiotic treatment may be prescribed. This usually takes the form of a syrup or pill. However, it’s important to complete the entire course of antibiotics during the 7 to 10 days of treatment.
When does impetigo stop being contagious in children?
Healing usually occurs within a few days of starting treatment . The child will no longer be contagious when the skin lesions, whether blisters or scabs, disappear.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does impetigo last in children?
Impetigo usually clears up on its own after two to four weeks. If antibiotics are prescribed, the disease will resolve within a few days.
▷ Useful for you: Bacterial skin infections are typical in children
Does impetigo leave scars on the skin?
Yes, impetigo blisters and scabs on the skin can leave scars.
Can it be prevented?
This infection can be prevented by washing the wound or scratch on the skin with soap and water.
Is childhood impetigo dangerous?
Impetigo in children is generally not dangerous, although it is recommended to treat the infection appropriately to avoid a serious clinical picture.




















+ There are no comments
Add yours