The gallbladder is an organ located below the liver, but sometimes it presents problems and requires evaluations to determine the best treatment.
In a practical sense, to understand the function of the gallbladder, it’s important to recognize that bile is stored there, which flows through the ducts into the small intestine when food is being digested and helps with the digestion of fats, says Héctor Luna, a gastrointestinal surgeon and endoscopist at Clínicas Punto 10.
The main way to prevent this organ is to lead a healthy lifestyle, maintain regular physical activity, and eat a balanced diet. This includes consuming foods rich in fiber and healthy fats like fish oil and olive oil, as well as avoiding carbohydrates and refined sugar.
Gallbladder problems are more likely to occur when the flow of bile through the bile ducts is blocked. This is usually due to the formation of gallstones, or gallstones, and can also lead to cancer.
Gallbladder problems are less common in children and adolescents, although they are occurring more frequently, explains Dr. Eveline Shue in an article published in Healthy Children. She also states that one in five adults could experience gallbladder problems in later life.
The symptoms themselves could complicate a diagnosis, as they can be common among various diseases. Nausea, pain, vomiting, jaundice or yellowing of the skin, and low weight are all conditions that should be evaluated to determine the underlying pathology, explains Yendry Rojas, medical manager of oncology at AstraZeneca.
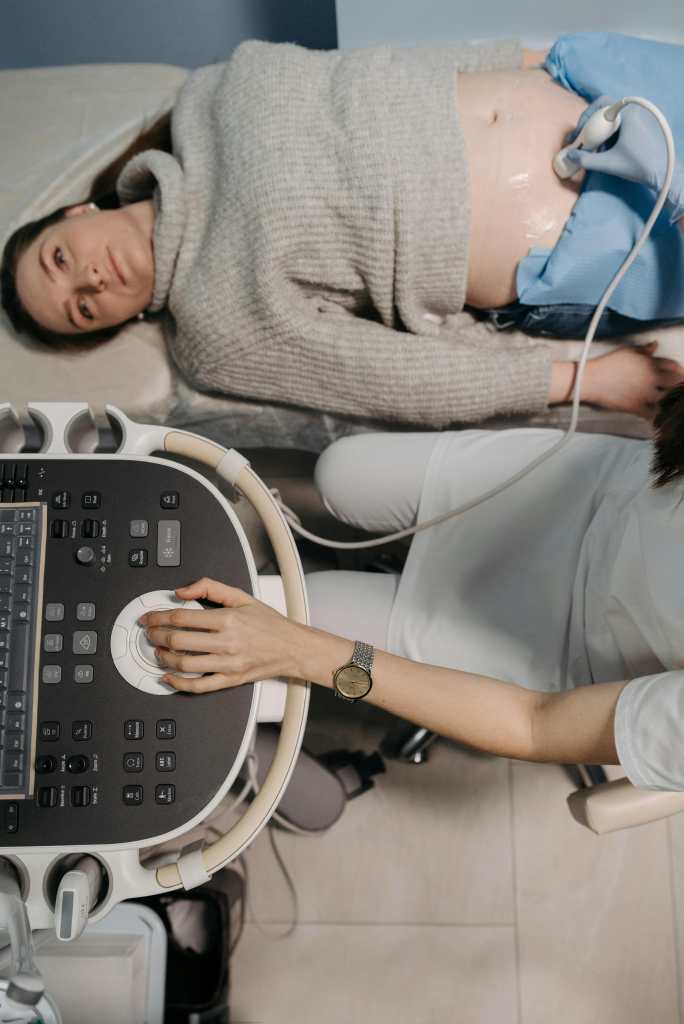
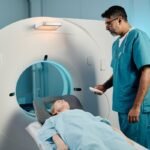
It’s important to recognize that various discomforts can occur in this area. When doctors suspect the problem originates in this region, an ultrasound is recommended; in some cases, an endoscopy may be required, as well as blood tests and radiological methods such as CT or MRI. This will depend on each patient’s case. A biopsy, i.e., a sample of the affected area may also be requested for evaluation.
Rojas explains that, in the case of patients, it’s also important to consider risk factors such as diabetes, advanced age, and a history of smoking, among others. When discomfort arises, it’s essential to consult a doctor so they can take the necessary action and avoid emergencies.
The most common diseases of the gallbladder
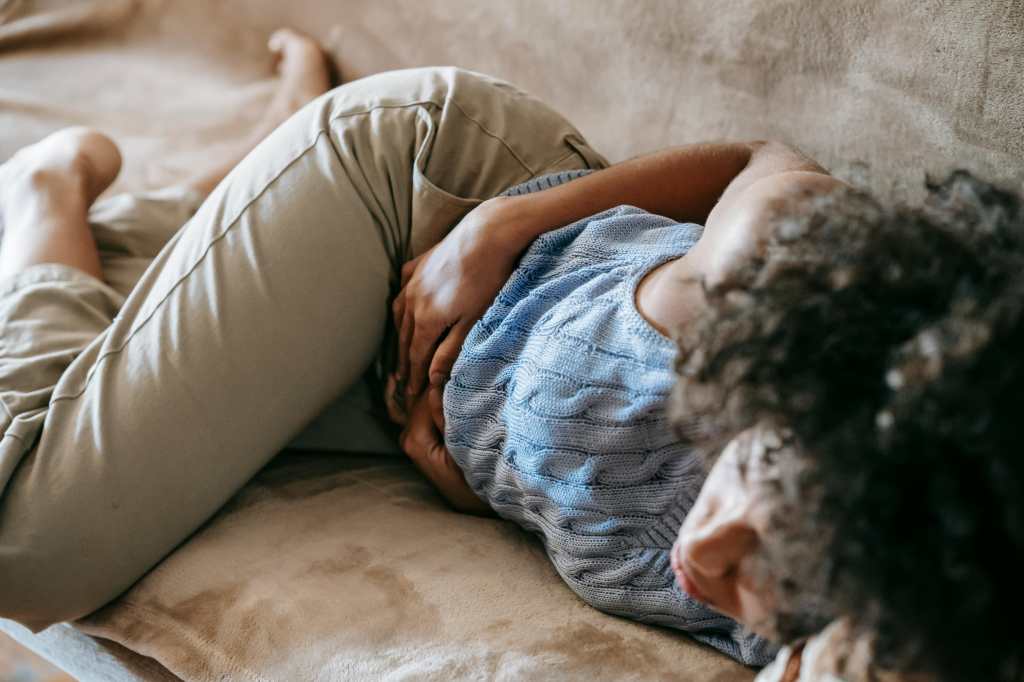

The experts consulted and the American College of Gastroenterology (CAG) offer more information on some diseases that occur in this organ.
Gallstones
This occurs when stones form inside the gallbladder, which can be microscopic or large. These develop due to imbalances in cholesterol levels (a component of bile) or genetic predispositions. “Normally, cholesterol dissolves (like sugar in water). The bile salts in bile are responsible for preventing cholesterol from precipitating, but when there is an imbalance in the ratio of cholesterol to bile salts, the cholesterol solidifies and forms stones,” notes the CAG’s official website.
When a stone tries to pass from the gallbladder, it can cause severe pain in the upper and middle abdomen. It also causes nausea, vomiting, and other discomforts. In some cases, emergency surgery to remove the gallbladder is suggested.
“70% of cases that develop this disease respond to environmental factors and 30% have a genetic component,” notes the Spanish Association of Gastroenterology, which points out, among other risk factors associated with the onset of cholelithiasis, being female, having multiple pregnancies, obesity, rapid weight loss, high triglyceride levels, a diet rich in animal fat, diabetes, genetic factors, prolonged fasting, total parenteral nutrition, cirrhosis, biliary strictures, congenital cysts, or chronic pancreatitis.
Acute biliary pancreatitis
This occurs when a stone passes from the gallbladder and becomes trapped in one of the bile ducts. The pain is persistent, and vomiting may also occur. Treatment ranges from pain medication and rest to emergency surgery to remove the stone and/or the gallbladder.
Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
The sphincter of Oddi regulates the flow of both bile and pancreatic juices into the intestine. If it contracts or narrows, it prevents proper flow and can cause pain. In some cases, surgery to cut the sphincter may be required.
Bile duct cancer
Rojas explains that, occasionally, abnormal cells develop in the bile ducts, the gallbladder, or some other structure within the bile duct. This type of cancer is rare and aggressive. Approximately 210,000 patients could be diagnosed with this type of cancer worldwide. Chemotherapy and other medications may be necessary for treatment. In some cases, it can be confused with liver cancer.
Chronic inflammation of the gallbladder is a common link among many of the risk factors for gallbladder cancer. Overweight, smoking and genetic factors also play a role.




















+ There are no comments
Add yours