The liver is one of the vital organs of the human being and hepatitis can affect it to the point of putting your life at risk. Preventing and detecting any disease in time is the most important thing for health.
These diseases affect the liver, which has nearly 500 functions. It is important in digestion, metabolism, and strengthening the immune system, to name a few of the main ones.
To learn more about our body, the liver weighs more than three pounds and is located in the upper right part of the abdominal cavity. It breaks down toxic substances in the body, which are eliminated through urine or stool; it stores vitamins, and iron and produces proteins. It also helps in the production of antibodies.
It is important to note that some people with hepatitis are asymptomatic and do not know they are infected. In the Americas, it is estimated that between 60,000 and 100,000 people die each year due to hepatitis.
What is hepatitis
Gastroenterologist Arturo Carranza explains that hepatitis means that there is inflammation of the liver and this can be due to different causes, both viral and otherwise.
For example, excessive alcohol and some medications can inflame this organ. In this article, we will focus on viral infections, which are divided into A, B, C, D, and E.
A relevant detail is that when this inflammation is recent it is explained as acute hepatitis and processes that last more than six months are called chronic hepatitis.
What are the types of hepatitis?
Several types of these viruses affect the liver when it is through a virus.
Hepatitis A
It is the most common and only one that does not cause liver damage, and with appropriate treatment the liver will go down in weeks. It is transmitted by eating contaminated food or water and the probability of developing it increases if you have not been vaccinated.
This condition heals within a few days and usually does not cause major complications. Pregnant women or patients who suffer from diseases that compromise their immune systems must be careful with this disease, which could worsen under their conditions.
Hepatitis B
It can be prevented by vaccination. A percentage of patients who contract it are cured, but a number of them may develop chronic hepatitis. Without treatment, it develops into cirrhosis in 10 to 15 years. It is four times more contagious than the human immunodeficiency virus, HIV.
Hepatitis C
Ninety percent of those who contract the disease develop cirrhosis, and 5 to 10 percent recover. There is no vaccine because its molecular structure is constantly changing.
Hepatitis D
The hepatitis D virus requires the presence of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) to replicate. The World Health Organization explains that simultaneous infection is considered the most serious form of chronic viral hepatitis, given its faster progression to cancer and death from liver failure.
Hepatitis E
Like A, it is caused by the consumption of contaminated food or water.
What causes hepatitis
Hepatitis can be caused by infections caused by viruses (such as hepatitis A, B, or C), bacteria, or parasites.
As explained above, liver damage can also arise from alcohol, certain medications, or toxins (poisons).
What are the symptoms of hepatitis?
The manifestations of liver diseases are similar and diverse. The following are the most common:
- Jaundice or yellowish pigmentation of the skin and whites of the eyes.
- Ascites are swelling due to fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity.
- Increased blood pressure, dilated veins, and varicose veins form and the patient usually vomits excessive amounts of blood.
- Mental confusion because brain functions are impaired by the increase in toxic substances in the blood that the liver would have to eliminate. It can lead to hepatic coma.
- Problems in the circulatory system, and nausea, among others.
How to prevent or treat hepatitis
These diseases are preventable and controllable; there are effective vaccines against hepatitis A and B and cutting-edge treatments for hepatitis C.
In the case of hepatitis C, clinical trials and observational studies of patients treated with direct-acting antiviral drugs show that a sustainable virological response, with elimination of the virus from the body, can be achieved in about 95% of cases, say experts from the Pan American Health Organization.
Ongoing research into the treatment of hepatitis B is also very promising. The availability of an effective vaccine makes a substantial reduction in new hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections a possible goal.
Vaccines against hepatitis B, for example, are given to newborns and are free of charge nationwide. At three months of age, the hepatitis A vaccine is given. Adults receive three doses of hepatitis B and two doses of A.
Carranza explains that some people do not have symptoms. The idea is that in addition to vaccination, a general blood transaminase test should be performed annually, which helps monitor the health of the liver and is a support for diagnosing liver diseases such as viral hepatitis, alcoholic hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis, and cirrhosis, among others.
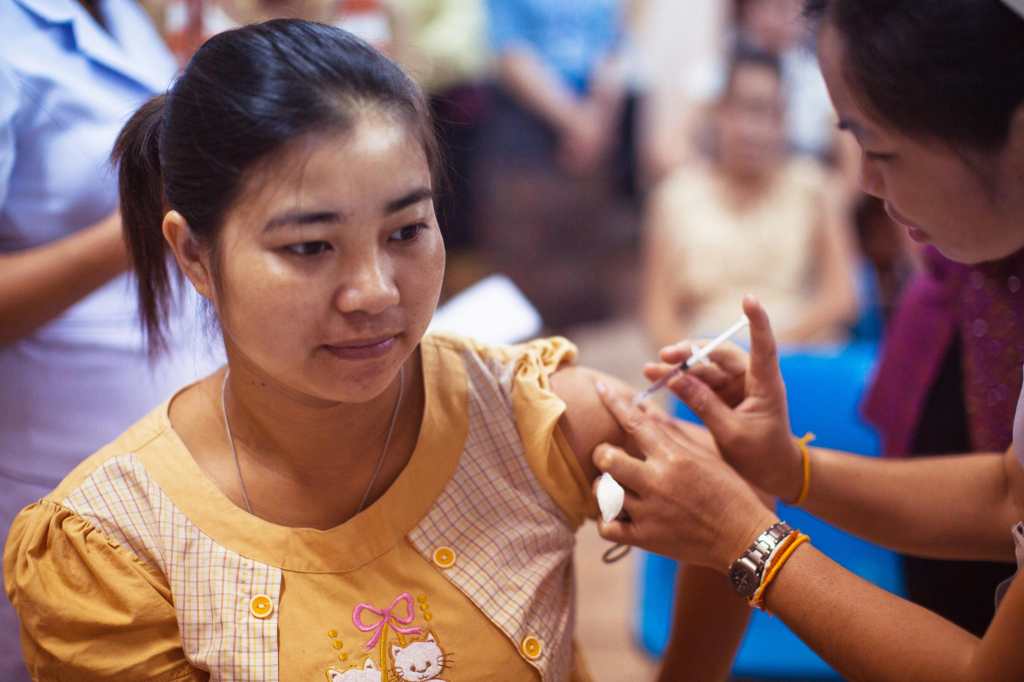

What to do if I have hepatitis
In the case of hepatitis A and E, recovery time is essential. The body will gradually recover and in the meantime, it is recommended to rest and take some medication for fever or nausea, or consult with the doctor if there are other symptoms that require support.
For hepatitis B, people need treatment for the rest of their lives. “The decision to start treatment depends on many factors, including whether the virus causes inflammation or scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), whether they have other infections such as hepatitis C or HIV, or whether their immune system is suppressed by illness or medications,” the Mayo Clinic website says.
Dr. Carranza adds that these treatments are intended to prevent the liver from reaching the level of cirrhosis or cancer. In the case of hepatitis C, antiviral drugs are recommended.
In severe liver damage, a transplant is also an option.
Recommendations
In general, to maintain liver health, it is essential to eat a balanced diet, reduce alcohol consumption, not abuse medications with certain ingredients, protect yourself during sexual relations, not share needles and, in the case of hepatitis A and B, get vaccinated.


















+ There are no comments
Add yours