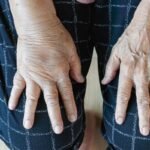
Eyebrow alopecia is a relatively common problem that often causes significant aesthetic discomfort to those who suffer from it.
This is because they greatly influence the perception of facial beauty. Furthermore, for a few years now, thick, full eyebrows have become a trend, as opposed to the thin, tightly plucked eyebrows that were popular some time ago.
But beyond aesthetics, we must remember that this part of the body has a protective function that should not be underestimated. Eyebrows complement the eyelids and eyelashes in protecting the eyes.
Specifically, they filter solar radiation and prevent sweat, rain, dust, or other wind-blown particles from entering or hitting the ocular surface.
Furthermore, eyebrows play a key role in expressing our mood or feelings, such as surprise, anger, or doubt.
The causes of eyebrow loss can be very diverse, and treatment is complex. Therefore, a correct diagnosis is essential for achieving improvement.
Eyebrow alopecia: causes
It should be noted that eyebrow hair loss can be associated with more than 100 different types of alopecia.
At the same time, multiple diseases can cause this symptom, such as hypothyroidism, autoimmune conditions, or even emotional disorders.
Hence, the importance of a good differential diagnosis to implementing the most effective treatment for each case.
However, in eyebrow alopecia, the most common causes are usually the following:
- Aging. The natural density of eyebrows decreases over time. Therefore, it’s common to notice eyebrow loss with age.
- Alopecia areata. The most common location of alopecia areata is the scalp, but it can occur on any other hairy part of the body.
Sometimes, alopecia areata affects only the eyebrows and/or eyelashes, affecting only these parts of the body. When this happens, bald patches appear, devoid of hair.
- Frontal fibrosing alopecia . This type of scarring alopecia is characterized by hair loss at the front of the hairline, but also by eyebrow loss .
This symptom can be observed in a high percentage of those affected, and some studies have even estimated that it could be present in up to 95% of cases.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia in the eyebrows is often the first symptom of the disease.
It doesn’t usually involve complete hair loss, but rather manifests primarily as a loss of hair density in the area. It isn’t accompanied by an inflammatory reaction or scaling.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia is more common in women after menopause, but it can occur at any age and can even cause eyebrow alopecia in men.
- Hair removal. Continued use of tweezers, waxing, or other pulling hair removal methods is a common cause of eyebrow hair loss.
Especially if it has been done with excessive force or frequency.
- Trichotillomania. This emotional disorder involves compulsive hair pulling, including eyebrow and eyelash hair, and is one of the main causes of stress-related hair loss.
It usually appears alongside anxiety disorders or in cases of obsessive-compulsive disorder.
- Dermatitis. Both atopic dermatitis and seborrheic dermatitis can be associated with eyebrow alopecia.
- Hypothyroidism. Eyebrow alopecia in hypothyroidism is a little-known symptom.
If it occurs, it is usually alopecia of the ‘tail’ of the eyebrows and affects the sides.
- Autoimmune diseases . Beyond alopecia areata and frontal fibrosing alopecia, there are many other autoimmune diseases that can cause eyebrow loss. Lupus is one of them.
- Medications . Certain treatments can cause temporary or permanent eyebrow loss. For example, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, which are used in cancer treatments.
Also, high doses of niacin or retinol.
- Genetic dermatoses. Eyebrow alopecia in newborns can be a symptom of numerous hereditary diseases and generally has a poor prognosis.
However, the birth of a child without eyebrows doesn’t always have to be a warning sign. It can be a normal variant, with no clinical significance.
- Infections: Leprosy and syphilis are infections that can also manifest with hair loss in the eyebrows.
- Neoplasms. Although less common, skin cancer is another possible cause of eyebrow alopecia. This symptom is primarily seen in people with squamous cell carcinoma or basal cell carcinoma.
It can also be a manifestation of malignant melanoma or a consequence of other cancerous processes.
Treatment for eyebrow loss
Sometimes eyebrow loss can be permanent. However, in most cases, the hair will regrow naturally, or its growth can be stimulated with the help of various treatments.
When eyebrow alopecia is a symptom of underlying conditions, such as hypothyroidism or anxiety, these conditions will also need to be treated.
Although treatment for eyebrow loss will depend on the cause, the main solutions for alopecia in this area of the face are the following:
- Topical vasodilator . This medication improves follicular growth by promoting blood flow and oxygen delivery to the hair follicle.
- Prostanoids . These drugs have the ability to promote hair growth, which is why they are frequently used to treat eyebrow and eyelash loss .
- Anti-inflammatories and immunomodulators. Both groups of medications, applied topically or as injections, may be indicated for eyebrow alopecia that causes inflammation and is associated with autoimmune disorders.
- Minoxidil. This drug appears to prolong the anagen phase of the hair follicle (growth phase) and promote hair regrowth.
- Eyebrow transplant. When the main treatments for eyebrow alopecia are insufficient, a transplant may be considered.
The transplanted hair is usually extracted from the nape of the neck, although in men it is sometimes obtained from the arms, chest, or beard.




















+ There are no comments
Add yours