Sexuality is an encounter of intimacy and pleasure, but without responsibility, it could turn into infections and diseases that lead the person to be in a labyrinth, sometimes with no way out.
Sexually transmitted infections and diseases are spread through sexual contact. The organisms that cause these conditions are passed from one person to another through semen, blood, vaginal fluid, and other bodily fluids.
The World Health Organization, WHO, explains that there are more than 30 viruses, bacteria, and parasites that are known to be transmitted through sexual contact. The hardest news is that they have been linked to different sexually transmitted diseases.
There are eight of the most common types, four of which are curable: syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis.
Hepatitis B, herpes simplex virus (HSV or herpes), HIV, and human papillomavirus (HPV) are considered incurable infections, although there are treatments that seek to improve the quality of life of patients diagnosed with them.
STIs are predominantly spread through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. However, there are also non-sexual means such as blood transfusions or blood products, and others are transmitted during pregnancy or childbirth, from mother to child.

Gynecologist and obstetrician Ronaldo Retana says that each disease has different symptoms, but it is vital to go to the doctor as soon as vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor appears.
In men, the reasons for consultation should be when there is urethral discharge or burning, as well as genital ulcers.
Margarito Castro, a gynecologist, obstetrician, and expert in human sexuality, explains that in 35 years of working in the medical field, these diseases are still common and that adolescents are also developing diseases due to having more and more oral and anal contact.
“They believe that by having sex this way they do not lose their virginity, but diseases are not transmitted only through intercourse but also through bodily fluids,” the doctor added.
What are the symptoms of each disease?

Pay attention to the signs of these infections and sexually transmitted diseases. If you have any of the symptoms, seek help immediately. Once it is confirmed that you have one of them, your partner or partners must be also aware of this condition.
Do not self-medicate because this could have other consequences. A diagnosis by a professional is necessary to avoid putting your health at risk.
- Syphilis, gonorrhoea and chlamydia
According to the WHO, it is estimated that each year, some 357 million people contract one of these four diseases.
Gonorrhoea and chlamydia are the main causes of pelvic inflammatory disease, adverse pregnancy outcomes, and infertility. These two infections have similar characteristics, at first, there may be no symptoms and then vaginal discharge, pain when urinating, vaginal bleeding between menstrual periods, as well as rectal bleeding and discharge or pain may occur.
Syphilis has other symptoms. A painless sore may appear, and if left untreated a rash may appear, usually appearing on the soles of the feet and the palms of the hands, warts on the vulva, and flu-like symptoms may also appear. In its late stages without treatment, it is associated with heart problems, neurological problems, blindness, and paralysis and can cause death.
Treatment is with antibiotics. - Trichomoniasis
This is caused by a parasite. Symptoms may appear between 5 and 28 days after infection. There is a greenish or yellowish vaginal discharge, pain during intercourse, vaginal odor, pain when urinating, itching, burning when urinating or ejaculating, and discharge from the penis. It is also treated with antibiotics but may reoccur after three months. For this reason, it is essential that the partner(s) also receive treatment. - Hepatitis B
This liver infection is caused by a virus. Its presence increases the risk of developing liver failure, liver cancer, and cirrhosis. Vaccination can prevent it, but once infected there is no cure. People have abdominal pain, dark urine, fever, joint pain, nausea, weakness, and yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes. It is contracted sexually through contact with blood, semen, and other bodily fluids of an infected person. It is also related to the use of needles from mother to child, during childbirth. - Herpes simplex virus type 2
The number of people with genital HSV (herpes) infection exceeds 500 million. It is important to know that this disease and syphilis increase the risk of contracting HIV.
This is an infection that is transmitted exclusively through sexual contact. There is no cure. Symptoms may be mild at first, genital or anal ulcers may appear, and may be associated with fever and pain. Antiviral drugs are used, which reduce symptoms but do not cure the infection. - HIV
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus damages the immune system by destroying white blood cells that help fight infections. In 2018 alone, it is estimated that 1.7 million people were infected. It is transmitted sexually, by sharing needles, and pregnant women can infect their babies during pregnancy or childbirth.
At first, the symptoms are related to flu, fatigue, and swollen glands. Frequent or unusual infections, heart, kidney, or liver diseases, among others, may appear. Over time, the body becomes more vulnerable to new diseases or serious infections. Different treatments seek to give people a better quality of life. - Human Papillomavirus, HPV
The number is alarming, HPV infection causes 528 thousand cases of cervical cancer and 266 thousand deaths annually. HPV is a group of viruses, there are more than 200 types and almost 40 of them affect the genital area. It can cause several types of cancer, including cervical, anal, vulvar, vaginal, penile, and some oral and throat cancers. Warts may appear in some people. As a preventive measure, it is suggested to use the vaccine before starting sexual life and also to have an annual evaluation with a pap smear.
Prevention that has challenges
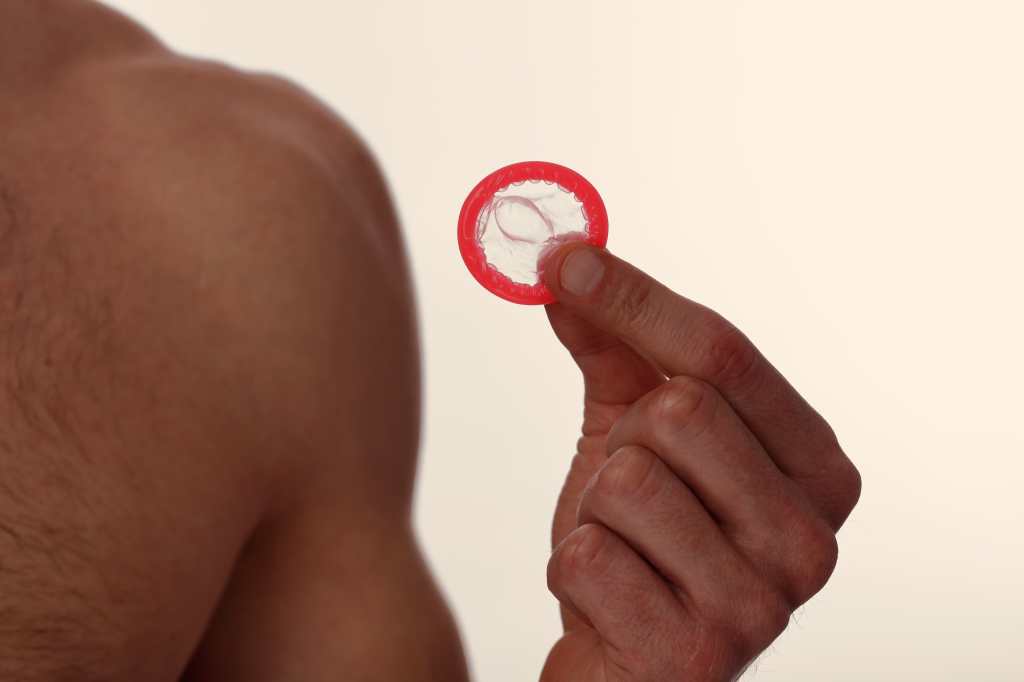
Without a doubt, the condom is one of the most important elements when it comes to prevention because it protects against pregnancy and more than 98% of the time against contracting some diseases. It is not completely safe.
Using them correctly means placing them before penetration, when the penis is erect, and removing them after ejaculation.
But sometimes there is some flirting in intimate areas and it is not until the moment of penetration when the fluids have already been part of the encounter, says Castro.
Other ways to ensure that you do not become infected include abstinence and delaying the age at which you start having sex, using a condom even with a stable partner, and reducing the number of sexual partners.
The experts consulted suggest that education is the key point to avoid further infections. “We are leaving young people without guidance when we do not talk about it at home or give them tools to be aware and have their own responsible opinion about sexuality,” says Castro.
“Promoting values and creating a space to talk about them begins at home and should be extended to other spaces,” Retana adds.
Herbert Bran, coordinator of community programs at Aprofam, explains that they have a program that seeks to train young people so that they can bring more accurate information to their peers.
Among the topics that adolescents learn are gender, sexuality, life plan, sexual and reproductive rights, as well as sexually transmitted infections, among others, Bran adds.
In 2019, nearly 350 adolescents were trained and this number is expected to multiply by the end of the year.
Bran adds that there is a belief that we are “supermen and superwomen” because this type of sexually transmitted infection cannot happen to us. “This is the biggest myth, believing that it only happens to promiscuous people or people with other sexual preferences, but STIs do not recognize age, gender or race…we are all exposed to them,” he concludes.























+ There are no comments
Add yours